|
constant |
the characteristics or elements that remain the same |
|
coordinate |
one of a set of numbers used to identify the location of a point
on a graph |
|
dependent variable |
a variable in an equation with a value that is determined by
mathematical operations on other variable and constant values
in the same equation |
|
graph |
a visual representation of a relationship between variables |
|
independent variable |
a variable in an equation that is assigned a value rather than
having a value that is determined by mathematical operations
on other parts of the same equation |
|
maximum point |
point on the curve with the highest y-coordinate and a
slope of zero |
|
minimum point |
point on the curve with the lowest y-coordinate and a
slope of zero |
|
negative slope |
the line is sloping down to the right, the slope is negative
(-) |
|
origin |
the point where the two axes intersect. The origin is also identified
as the point (0, 0). |
|
point of tangency |
the point where the curve and the tangent meet |
|
point |
the basic relationship displayed on a graph. Each point is defined
by a pair of numbers containing two coordinates. Each point is
identified by both an x and a y coordinate. |
|
positive slope |
the line is sloping up to the right, the slope is positive (+) |
|
slope |
how much one variable (y) changes in relation to the
change in another variable (x). The slope of a line is
the ratio of the ratio of its vertical change (rise) over its
horizontal change (run) as we move from left to right on the
line. This can be written as follows:
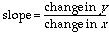 |
|
tangent |
a straight line that touches a curve at a single point and does
not cross through it |
|
variable |
the generic term for any characteristic or element that changes |
|
x-coordinate |
the value that tells you how far from the origin the point is
on the horizontal, or x-axis |
|
y-coordinate |
the value that tells you how far from the origin the point is
on the vertical, or y-axis |
|
y-intercept |
the point at which the line crosses the y-axis. The y-intercept
is the value of y when x is equal to zero. |